Risk-on currencies versus safe havens like gold
These two ways are often used to see how people feel about the market, one when the economy is doing great and the other when it's struggling.
Risk appetite works during economic growth. Traders buy high-yield currencies such as EUR and GBP. They sell low-yield ones like USD and JPY.
Risk Averse
Risk Averse is a strategy that traders use during economic recession time: in this strategy the traders will sell the high yielding currencies in favor of buying safe haven ones like USD and JPY, and safe haven commodities like Gold.
Speculation and Trading with This Strategy
Risk appetite helps assess general market sentiment. Speculative traders use this information to decide which currencies to trade and in which direction to execute their trades.
We shall look at a few examples that try to explain the general market direction of a currency in relation to another. Also we shall look at example of commodities that are also now traded in the Forex Market.
Risk Appetite has two sides, these are:
EUR, GBP, AUD, on one side
USD and JPY on the other side
Economic Boom
During periods characterized by robust Economic Expansion, the EUR, GBP, and AUD become particularly desirable assets, primarily because their associated interest rates are elevated - hence their designation as higher-yielding currencies. The fundamental basis for this 'higher-yielding' label is the carry trade mechanism, where trading these currencies generates supplemental earnings derived from holding the Interest rates by simply purchasing them.
Open a Trading Account in Just 5 Minutes: Open Your Forex Account Today
During periods of economic expansion, interest rates for these currencies can climb as high as 6% for the Australian Dollar and between 3% and 5% for the Euro and GBP. This implies that by year-end, holdings for traders retaining these currencies could see a 6% appreciation. Given that this is Forex trading involving leverage, consider a modest leverage of 10:1: that 6% return is then multiplied tenfold, resulting in a 60% return on investment. This is a strategy frequently adopted by hedge funds that acquire and hold currencies for years.
For example the image below, shows the GBP when its Interest rate was about 4.5 to 5 % and this helped fuel risk appetite one of the factors being that this was a higher yielding currency. This made the GBP to go up about 10,200 Pips (102,000 Pippetes, if using the 5 decimal points quoted by brokers of now, that time it was 4 decimal quotes). This is equal to 102 cents, or 1.02 dollars.
One dollar does not seem like a big amount. But when you use a 10:1 borrowing ratio, it turns into a large sum. This shift took place from 2000 to 2006, over six years, with 5% interest each year. That adds up to 30% total from interest over the time. Apply the 10:1 ratio, and the return jumps to 300%. This does not even include the gains from the 10,200 pips as the GBP gained value against the JPY.
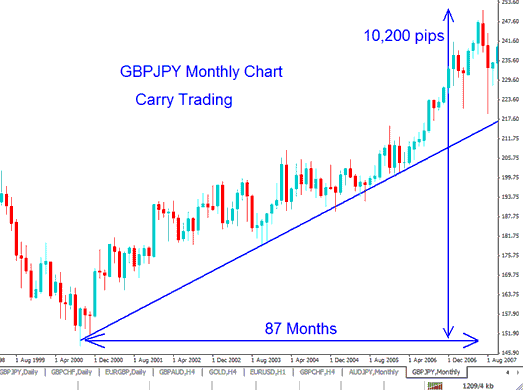
High-yield currencies draw traders in boom times. High rates boost risk appetite. These currencies gain value over low-rate ones. Think of bank accounts. One pays 5% interest, another 1%. Folks pick the better rate. Same goes for currencies with top yields.
When there is risk appetite:
EURUSD - Bullish
GBPUSD - Bullish
AUDUSD - Bullish
EURJPY - Bullish
GBPJPY - Bullish
AUDJPY - Bullish
NZD may also be added onto the list of higher yielding currencies because it is also one that has got a high interest rate - therefore traders may also trade NZDUSD and NZDJPY as bullish.
Economic Recession
In a recession, risk drops. Traders close high-yield currency spots and shift to US dollar and gold. Why?
US Dollar is the most stable currency worldwide, held as reserve by most banks and central banks all over the world, thus US Dollar would still be the last currency standing as it is the most hardest to dispose as everyone, every corporation, every commercial bank, every central bank has it. So in recession time when there is uncertainty, those who know, the economists would rather be holding on to USD rather than any other. This is known as Safe Haven; The USA Dollar is a safe haven - in times of economic recession traders will flock to the safe haven currencies - the USD. Therefore the value of USA Dollar will keep moving up in times of recession. The more the recession the more the US Dollar gains value, even if the Recession is hardest in USA, US Dollar will not lose value due to and because of this, US Dollar will gain more and more value, because it's the safest option. Vice Versa, if US Economy does very well, people will lose the dollar in favor of others that are higher yielding. That is why when the US economy is doing good and also all other Economies are doing good, other currencies such as GBP, EUR, AUD will gain on the USD, the USA Dollar might even lose value against these higher yielding currencies.
It is because of this reason that when recession hit in 2007, risk appetite became risk averse and the above investors closed all their buy positions and they started favoring buying the JPY and the USD which gained back all the value.
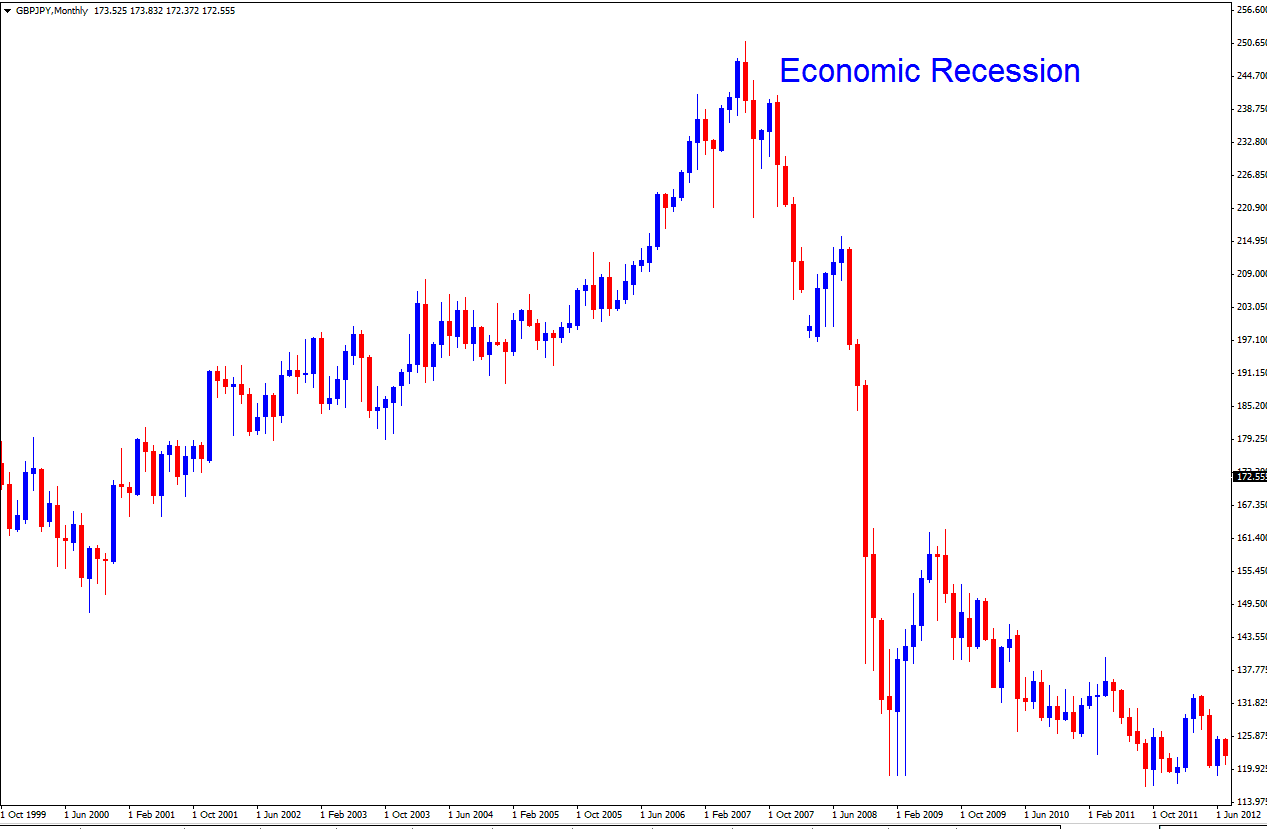
The JPY - Japanese Yen is also in the same category of Safe Haven Currency and will generally follow the same pattern with the USD, in economic boom other currencies gain value on JPY, in recession time people flock to the JPY, due to and because of its safe haven status.
For Commodities Gold, Silver
Gold, Silver on one side
USD on other side
Economic Recession
Central banks employ gold as a reserve asset and a store of value intended to underpin the worth of their national currencies. Typically, most central banks maintain gold reserves valued comparably to the aggregate amount of currency actively circulating within their domestic economies. This practice stems from the principle that every unit of legal tender must represent tangible value, corresponding to - and not exceeding - the worth of all goods and services available in that economy: exceeding this risks triggering inflation. Occasionally, central banks will also choose to officially back their circulating money supply with their gold reserves.
Gold acts as a safe spot in tough times, now as a good rather than money. During recessions, risk-shy people buy it up. This pushes gold prices higher.
In the 2007 recession, traders and investors turned cautious. They started buying gold. Brokers offered it as a trading tool back then. More folks got involved by snapping up online contracts. They held value in those contracts, not the actual metal. This sparked extra trades in gold. Prices shot up as investors picked this metal to protect their wealth.
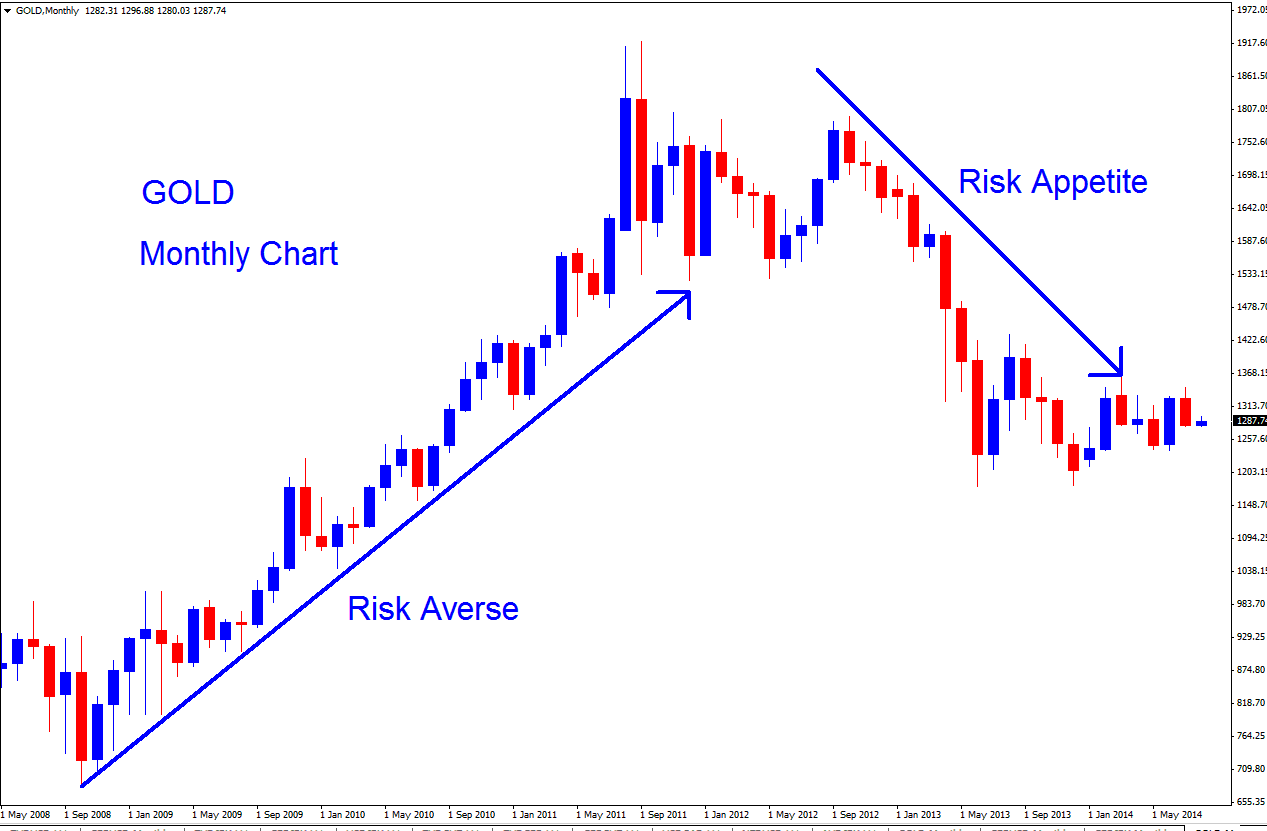
After the economy seemed to get better in 2012, investors became more willing to take chances, wanted to take risks, and started getting rid of their Gold Contracts. They did this so they could buy currencies that would give them better returns, because the economy was improving, meaning it would soon be safer to hold currencies that offered higher investment gains. As more and more investors stopped avoiding risks and started seeking them out, they closed their Gold Positions, which pushed the price of this item even lower.
However: Gold may also gain in value due to demand of the commodity when there is economic growth because people may start buying more jewelry. Hence, Gold may not necessarily follow this sentiment of risk appetite and risk averse all the time.
When there is risk averse:
EURUSD - Bearish
GBPUSD - Bearish
AUDUSD - Bearish
EURJPY - Bearish
GBPJPY - Bearish
AUDJPY - Bearish
NZD could be included in this list, enabling traders to also consider trading NZDUSD and NZDJPY as bearish options.
Commodity Oil
Commodity Oil is the Opposite of Gold
Economic Boom - Prices of Oil go up because there is more demand for Oil as Economies expand people have more to spend either factories are producing more using more energy and more and more people buying vehicles demanding more fuel.
It only takes five minutes to open a trading account, so get started early - open your forex account now.
During an economic recession, oil prices typically decline due to decreased demand. Vehicle owners often find themselves lacking funds for fuel, leading to reduced demand for products from factories and consequently lower production, which results in diminished fuel demand.
More Lessons:
- Methods for Adding Indicators to Charts within the MT4 Platform
- Aroon Oscillator Forex Technical Indicator Example Explained
- Trading Indexes Using Bollinger Band Squeeze Strategies
- Short Term Stock Index Trading Techniques Utilizing Moving Averages (MAs) for Indices
- Examples of Trading Methods and Techniques for Beginners
- How to Add MACD Indicators to XAU/USD Charts on MT4
- RSI Overbought and Over-sold Levels: RSI 70 and RSI 30 Levels
- Application for Calculating Position Size in Gold
- Darvas Box as an Automatic Trading System


